Studio RM Pro and Studio RM 1.12 – Major Release
Datamine is proud to announce the upcoming version of Studio RM Pro 1.12 and Studio RM 1.12, to be released in July 2022. As always, this version will be made available to maintained customers, giving them access to a vast range of new and updated functionality.
- Swipe Selection and Partial Drillhole Selection
In Studio RM 1.12, you will find interacting with drillhole data is more intuitive. Instead of selecting an entire drillhole, individual sample selection has been set as the default behaviour. This gives you more control to inspect and interrogate your drillholes. You can also now select any data using a swipe selection, which acts like a paintbrush across your data for identifying data in complex spatial zones.
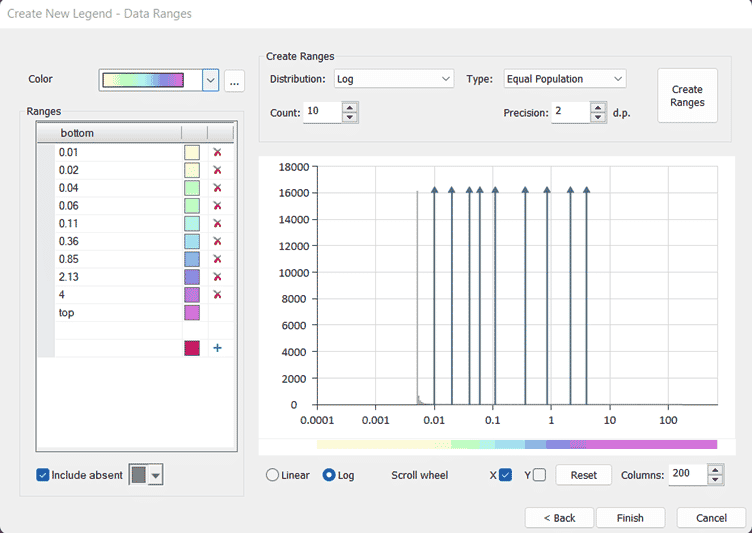
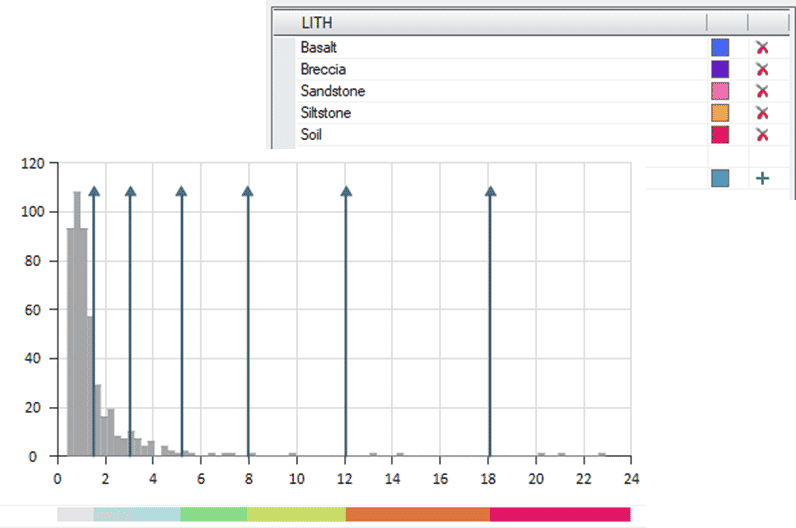
- Create New Legend
A new method for creating legends has been added to Studio RM 1.12. This easy-to-use tool comes packed with features that make creating informative legends from scratch a really simple operation. For numeric data, you can see a histogram of your data relative to the colour bins, change the bins directly on the histogram and edit the bin data for creating a legend that corresponds well with your data. External colour pallets may be shared between users.
- Block Model Rendering
The rendering performance of models when being displayed as blocks has been significantly improved. This means that you can now manage and interrogate even larger block models in 3D.
- Geology Modelling Tools
This release has further improvements to the categorical and grade shell commands, which use machine learning to fit surfaces around irregular geological zones. This type of modelling is suitable for modelling irregular intrusions, structurally controlled orebodies, or grade shells above a cut-off value.
This latest version has increased the speed and accuracy of models when using multiple ellipsoids. Ellipsoids are easy to edit and are used to control the orientation and overall shape of the ore body at separate locations.
There have been minor enhancements to the vein modelling and contact surface modelling tools, with the introduction of an extension distance around the proto. This creates a vein or surface slightly larger than the size of the proto, to reduce any potential edge effects created when the wireframe is smaller than the block model.
We have also added smart snapping controls to the contact surface, so a user can precisely control where a surface passes when intersecting ignored units. They can also control if a surface passes above collars or below end of hole positions or exactly through these points.

- Advanced Estimation Improvements
In this release, we have added some major functionality to COKRIG, which runs faster grade estimation using multithreaded processes.
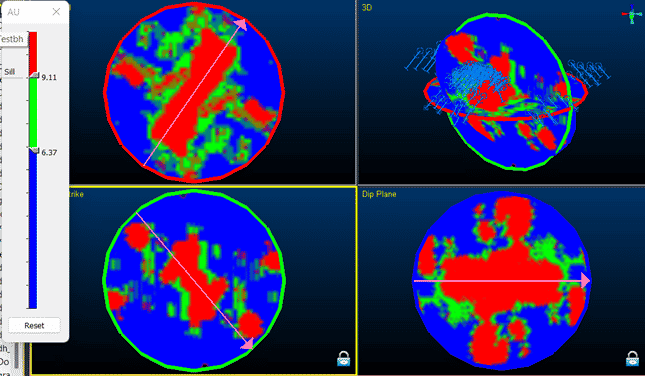
- Investigate Anisotropy
This version introduces a method for determining the anisotropy of the sample data. This approach uses non-perpendicular sections to look at the variogram contour map in the horizontal, across strike, and if required, the dip plane. This improved methodology makes it easier to determine the orientation of the direction with most continuity, so variograms are created perpendicular to these.
- Dynamic Anisotropy
We have added Angled Estimation, along with a new workflow to guide you through setting up a block model to be estimated using Dynamic Anisotropy. This makes it easier to use Dynamic Anisotropy to improve your grade estimates.
You can now use dynamic anisotropy with the basic estimation methods, like nearest neighbour and inverse power of distance. Dynamic Anisotropy no longer requires three angles – it can be run with one, two or three; and the missing angles (if present) will be taken from the search/variogram as appropriate. This flexibility allows for detailed control when variations in the orientation are seen in fewer than three directions.
- Empty Zones
We have also added the facility to use empty zone fields. An empty zone field is a zone field that is not specified and acts as a catch-all to apply the same estimation parameters to all the un-estimated zones. There are some new output statistics – the minimum distance to samples and the average distance which may assist with classification of reserves.
- Importing variograms from Supervisor
We have extended the functionality to import from Supervisor, which now includes importing normal score variograms and cross-variograms (compatible with the current version of Supervisor; v8.1.15).

Customer Focus
Datamine’s development is customer-driven, and our focus is on building software that makes doing your job as a geologist easier. If you have suggestions, feedback or ideas for our products, please don’t hesitate to contact your local Datamine office, we will be pleased to hear from you.



